Installing Phpmyadmin On Solaris 10 Network
Sun Solaris 10 - How to Setup a SAMP Server + VSFTP + Phpmyadmin (Solaris Apache2 Mysql5 Php5). I am installing OracleDeveloper software on a Sol 10 server. The process requires an X-Windows GUI display, but I don't remember how to set it up. Thank you in advance. Reverse dependencies ( 0 ) Reverse dependencies are Solaris packages that depends on phpmyadmin.
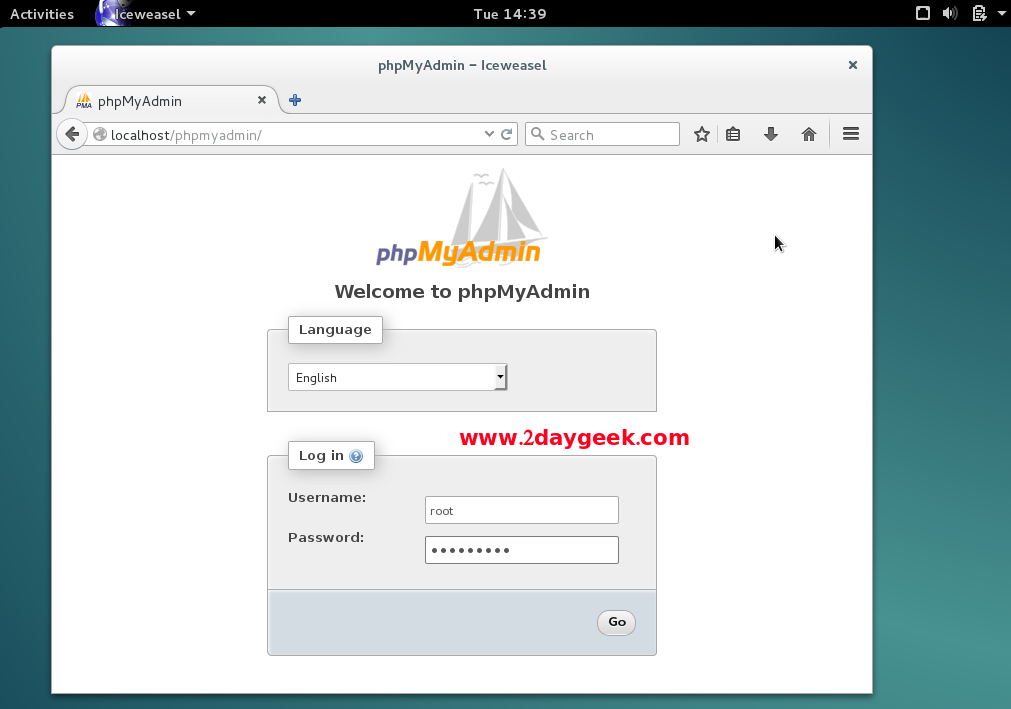
Nov 05, 2010 If using phpMyAdmin create a file called.htaccess in the phpMyAdmin install directory and add these lines: This makes it so that phpMyAdmin can only be accessed from the localhost. If using phpMyAdmin create a file called.htaccess in the phpMyAdmin install directory and add these lines: This makes it so that phpMyAdmin can only be accessed from the localhost. Home Universe Sun Solaris 10 – How to configure the server SAMP + VSFTP + Phpmyadmin (Solaris Apache2 Mysql5 Php5) Sun Solaris 10 – How to configure the server SAMP + VSFTP + Phpmyadmin (Solaris Apache2 Mysql5 Php5). Svc: / network / cswmysql5: default The default directory for the database was not found.
How to Configure a Physical Interface AfterSystem Installation
Configuring Solaris 10 jumpstart server and client. Jumpstart makes the life of a system admin easy by automating the installation of Solaris operating system. With jumpstart you can do an unattended solaris installation with unbundled softwares. Epson windows 7 printer drivers.
Use the next procedure for configuring interfaces. If you are usingthe Solaris 10 3/05 release, use the procedure How to Add a Physical Interface After Installation in Solaris 10 3/05 ONLY.
Before You Begin
Determine the IPv4 addresses thatyou want to use for the additional interfaces.
Ensure that the physical interface to be configured has beenphysically installed onto the system. For information about installing separatelypurchased NIC hardware, refer to the manufacturer's instructions that accompanythe NIC.
If you have just installed the interface, perform a reconfigurationboot before proceeding with the next task.
On the system with the interfaces to be configured, assume thePrimary Administrator role or become superuser.
The Primary Administratorrole includes the Primary Administrator profile. To create the role and assignthe role to a user, see Chapter 2, Working With the Solaris Management Console (Tasks), in System Administration Guide: Basic Administration.
Determine which interfaces are currently installed on the system.
Configure and plumb each interface.
For example, for qfe0 you would type:
Note –Interfaces that are explicitly configured with the ifconfig commanddo not persist across a reboot.
Assign an IPv4 address and netmask to the interface.
For example, for qfe0 you would type:
Note –You can specify an IPv4 address in either traditional IPv4 notationor CIDR notation.
Verify that the newly configured interfaces are plumbed and configured,or “UP.”
Check the status line for each interface that is displayed. Ensure thatthe output contains an UP flag on the status line, forexample:
(Optional) To make the interface configuration persist acrossreboots, perform the following steps:
Create an /etc/hostname.interface filefor each interface to be configured.
For example, to add a qfe0 interface,you would create the following file:
Note –If you create alternate hostname files for thesame interface, the alternate files must also follow the naming format hostname.[0–9]*, such as hostname.qfe0.a123. Names such as hostname.qfe0.bak or hostname.qfe0.old areinvalid and will be ignored by scripts during system boot.
Note,too, that a given interface must have only one corresponding hostname file.If you create an alternate hostname file for an interface with a valid filename,such as /etc/hostname.qfe and /etc/hostname.qfe.a123, the boot scripts will attempt to configure by referencing thecontents of both hostname files and would therefore generate errors. To preventthese errors, provide an invalid file name to the hostname file that you donot want to use in a given configuration.
Edit the /etc/hostname.interface file.
At a minimum, add the IPv4 address of the interface to the file.You can use traditional IPv4 notation or CIDR notation to specify the IP addressof the interface. You can also add a netmask and other configuration informationto the file.
Note –To add an IPv6 address to an interface, refer to Modifying an IPv6 Interface Configuration for Hosts and Servers
For Solaris 10 11/06 and earlier releases of Oracle Solaris 10,add entries for the new interfaces into the /etc/inet/ipnodes file.
Add entries for the new interfaces into the /etc/inet/hosts file.
Perform a reconfiguration boot.
Verify that the interface you created in the /etc/hostname.interface file has been configured.
For examples, refer to Example 6–2.
Example 6–2 Adding Persistent Interface Configurations
The example shows how to configure the interfaces qfe0 and qfe1 to a host. These interfaces remain persistent across reboots.
At this point, you would reboot the system.
After the system boots, you would then verify the interface configuration. Hp deskjet ink advantage 2060 driver download.
See Also
To configure an IPv6 address onto an interface, refer to How to Enable an IPv6 Interface for the Current Session.
To set up failover detection and failback for interfaces byusing IP Network Multipathing (IPMP), refer to Chapter 31, Administering IPMP (Tasks).
I have a mysql server already running on RHEL 5 server. I have other Solaris 10 and Solaris 11 machines (SPARC based T4-4 servers) which need to connect to the server. I downloaded a pkg (mysql-5.6.23-solaris11-sparc-64bit.pkg.gz) from MySQL CE downloads but it installed client as well as server on the Solaris machine. It only provided me two options: ALL or QUIT.
Are there any packages available for a client only installation? Or are there any configuration parameters for the same?
2 Answers
How To Enable Port 25 On Solaris 10
With Solaris 10 & 11, pkg should be available. Try to install the database/mysql-55/client package:
I would suggest the 5.6.23 MySQL client from OpenCSW, found here. Their package manager is fairly easy to use. I have no affiliation with OpenCSW and understand the reasons that other package repositories have become more commercial in nature, but appreciate the work that OpenCSW have done to keep free packages available for Solaris.